Beyond Putin: Russia’s Generations Y and Z

Of Russia’s 146 million citizens (if we include those in Crimea), 63 million—or 43 percent—are under 34 years of age. Of these, 30 million belong to Generation Y (millennials in their 20s and early 30s), 15 million belong to Gen Z (teenagers), and a further 18 million are part of the youngest generation (less than 10 years of age).
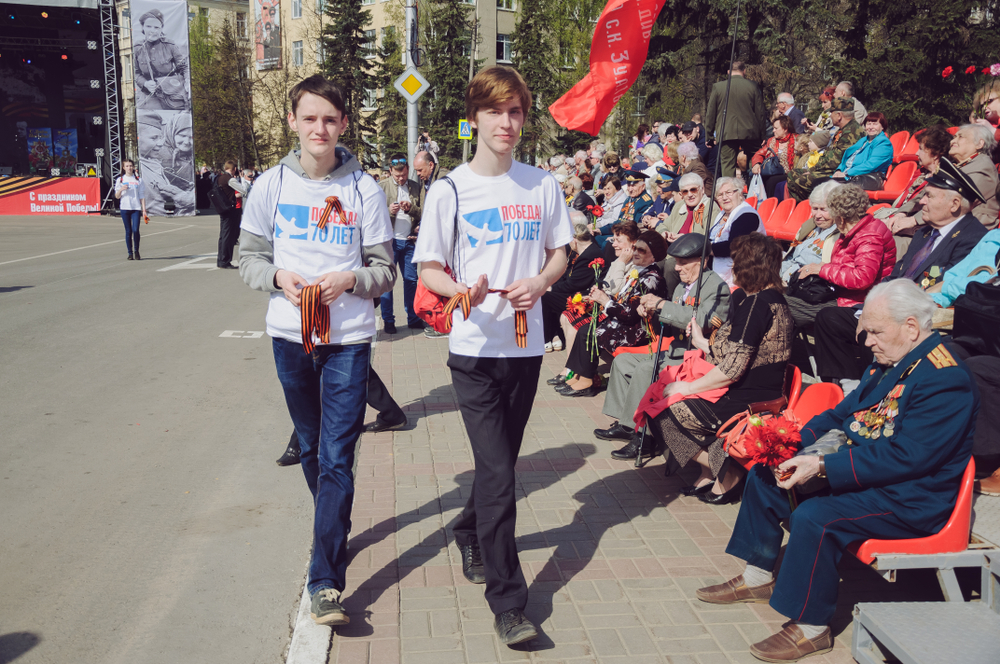

Russia’s youth have recently become the object of Western media interest with articles exploring everything from their support for President Vladimir Putin to their musical taste. Yet questions about Russia’s next generation remain largely understudied in Western academia (in contrast to its development in Russian scholarship), with only a handful of already dated analyses, a few studies on Russian students’ geopolitical visions, a couple of think tank reports, and a comparative book by Felix Krawatzek. The majority of these studies focus on interpreting the political role of Russia’s youth: for or against the Putin regime? Yet this politicization of our reading of young Russians misses the most interesting points: that one can be simultaneously for and against Putin, and that life is much more than formal political positions. First, Russia’s youth displays similar features to youth in other countries, chiefly its consumerism and social media savvy. Second, it is ambivalent on today’s Russia, both embracing it and taking critical distance from it. Third, the youth cultural scene—and especially the hip hop scene—is blossoming, becoming one of the most vivid contexts for expressing Russia’s evolving cultural norms and values.

Available in:
Regions and themes
Share
Download the full analysis
This page contains only a summary of our work. If you would like to have access to all the information from our research on the subject, you can download the full version in PDF format.
Beyond Putin: Russia’s Generations Y and Z
Related centers and programs
Discover our other research centers and programsFind out more
Discover all our analysesRussia, the Palestinians and Gaza: Adjustments after October 7th
The Soviet Union (USSR), and subsequently the Russian Federation as its internationally recognized legal successor, has consistently sought to play a visible role in efforts to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Deathonomics: The Social, Political, and Economic Costs of War in Russia
The report attempts to outline and examine a truly new phenomenon in Russian society, dubbed “deathonomics”—the making of a mercenary army against the backdrop of the Kremlin’s war in Ukraine, eventually replacing both the Soviet (conscript) and early new Russian (contract) armies. It notes that, by the end of 2023, this trend had turned the military service into one of the highest-paying professions in the country, something not seen in Russia on such a scale since the late 17th century.
Russia's Asia Strategy: Bolstering the Eagle's Eastern Wing
Among Russia’s strategic priorities, Asia traditionally played a secondary role compared to the West. In the mid-1990s, then Foreign Minister Yevgeny Primakov initiated a rapprochement with China and India. Then, in 2014, deteriorating relations between Russia and the West prompted Moscow to begin its “great pivot to the East”.
Kazakhstan After the Double Shock of 2022: Political, Economic and Military Consequences
The year 2022 represented a dual shock for Kazakhstan. In January, the country faced its most severe political crisis since independence, followed in February by Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, which cast uncertainty over the borders of post-Soviet states. These consecutive crises profoundly shaped Kazakhstan’s domestic and foreign policy.