Jammu and Kashmir in the Aftermath of August 2019

The abrogation of Article 370, which granted special status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), has been on the agenda of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) for many decades.
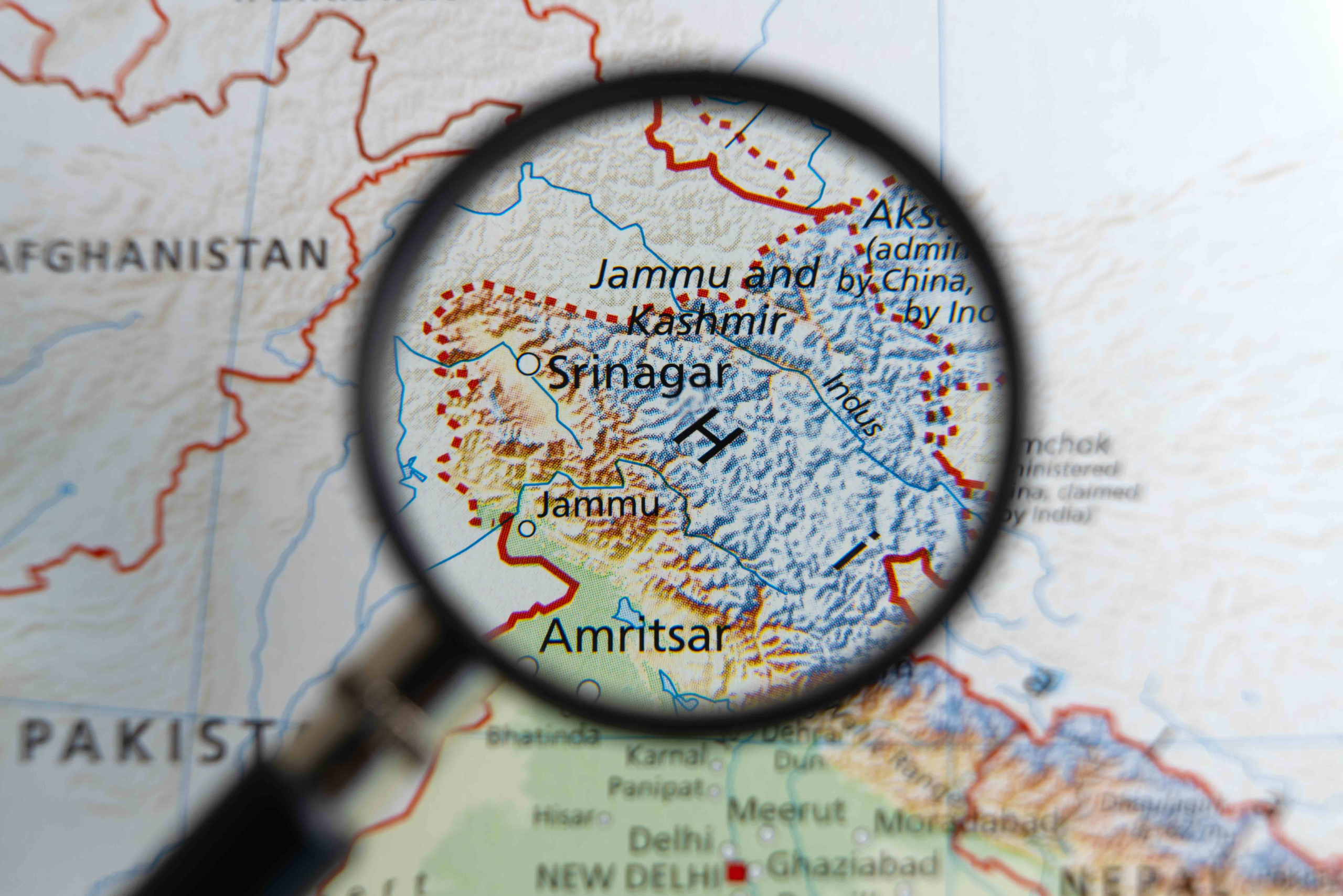
Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) was the only state that negotiated its accession to the Union of India in 1947. The instrument of accession signed by Maharaja Hari Singh on October 26, 1947 surrendered only four areas –defense, communications, foreign affairs, and finance–, giving the union government the power to decide on these matters, while the remaining areas were retained by the state.
When the Indian constitution was being framed, a temporary special provision under Article 370 was included to protect the autonomy, rights, interests, and identity of J&K. The state was also allowed to have its own separate constitution and flag, and many laws passed by the Indian parliament were not directly applicable to J&K unless the same was passed by its own legislature. Likewise, Article 35A, added to the Indian constitution through a presidential order in 1954, gave exclusive rights to the legislature of J&K to define the permanent citizens of the state and provide them with special rights and privileges. The article essentially reserved the rights over land, property, and jobs for the residents of J&K and debarred the citizens of other states from the same. However, the autonomy of the state was constantly emptied by successive central governments, culminating in the de-operationalization of Articles 370 and 35A in 2019.
On August 5, 2019, the Home Minister of India announced in parliament that the central government led by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) had abrogated Article 370 and repealed Article 35A through a presidential order. Concurrently, the Home Minister introduced the J&K Reorganization Bill 2019 to change the status of the state and divide it into two new union territories (UTs), i.e. the UT of Jammu and Kashmir and the UT of Ladakh. The bill was passed by the Indian parliament on August 6, 2019. While all this was being done, all of J&K was subjected to massive curfew and clampdown. The leadership across the political spectrum in J&K, including former chief ministers, were arrested, mobile and internet connectivity was entirely shut down, and a complete communication “gag” was imposed in the state. These measures, despite criticism, were taken to prevent any outbreak of violence.

Available in:
Themes and regions
Share
Download the full analysis
This page contains only a summary of our work. If you would like to have access to all the information from our research on the subject, you can download the full version in PDF format.
Jammu and Kashmir in the Aftermath of August 2019
Related centers and programs
Discover our other research centers and programsFind out more
Discover all our analysesEuropean Union-India: Lasting Rapprochement or Partnership of Convenience?
The partnership between the European Union (EU) and India has long been limited to economic exchanges. Its political dimension has gradually developed, culminating in its elevation to the status of a “strategic partnership” in 2004. However, the failure of negotiations for a free-trade agreement in 2013 slowed this momentum. Since the early 2020s, in an uncertain geopolitical context, bilateral rapprochement has gained new momentum.
Japan’s Takaichi Landslide: A New Face of Power
Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi has turned her exceptional popularity into a historic political victory. The snap elections of February 8 delivered an overwhelming majority for the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), driven by strong support from young voters, drawn to her iconoclastic and dynamic image, and from conservative voters reassured by her vision of national assertiveness. This popularity lays the foundation for an ambitious strategy on both the domestic and international fronts.
The U.S. Policy Toward Taiwan Beyond Donald Trump: Mapping the American Stakeholders of U.S.-Taiwan Relations
Donald Trump’s return to the White House reintroduced acute uncertainty into the security commitment of the United States (U.S.) to Taiwan. Unlike President Joe Biden, who repeatedly stated the determination to defend Taiwan, President Trump refrains from commenting on the hypothetical U.S. response in the context of a cross-Strait crisis.

China’s Strategy Toward Pacific Island countries: Countering Taiwan and Western Influence
Over the past decade, China has deployed a diplomatic strategy toward the Pacific Island Countries (PICs). This strategy pursues two main objectives: countering Taiwan's diplomatic influence in the region and countering the influence of liberal democracies in what Beijing refers to as the "Global South."