Europe
Europe is described here in a geographical sense. It is not limited to the European Union, and includes, for example, the United Kingdom and the Balkans. It remains central to international relations.
Related Subjects

Quest for Strategic Autonomy? Europe Grapples with the US - China Rivalry
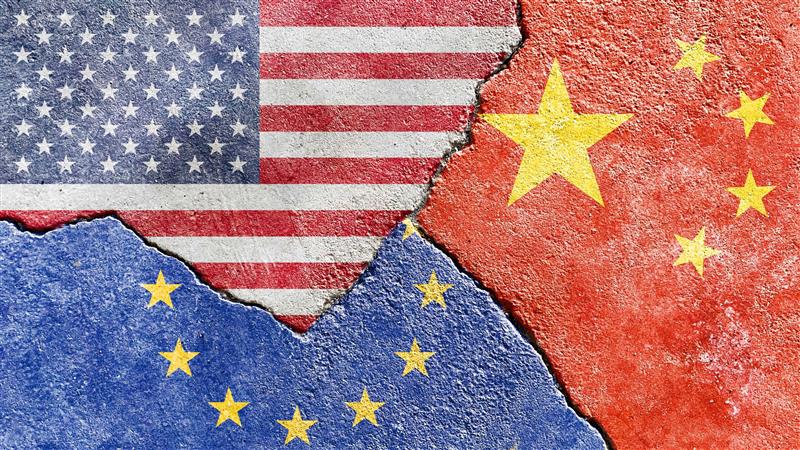

Building on the 2020 European Think Tank Network on China (ETNC) report, which assessed Europe’s positioning in this context, this edition re-examines the geopolitical landscape in light of the Covid-19 pandemic, Russia’s war in Ukraine and Donald Trump’s return to the White House. This report features 22 national chapters and one dedicated to the EU, analysing the evolution of Europe’s relations with Washington and Beijing, the range of approaches to dealing the US-China rivalry and how these are expected to evolve.
European Solar PV Manufacturing: Terminal Decline or Hope for a Rebirth?
While solar photovoltaic (PV) installations are booming in Europe (and in other parts of the world), the local industry is closing down. Over the past two years, the European installed solar PV capacity has been multiplied by two. On the other hand, the remaining European manufacturers of solar PV panels are dying.
NATO's New Ambitions for Space
Ahead of Russia's invasion of Ukraine, a devastating cyber attack targets Ukrainian army communications, exposing Western dependence and vulnerability to space technologies, and calling NATO's defensive posture into question.
How Macron and Scholz broke the Franco-German alliance at the heart of the EU
Breakdown of continental partnership is a threat to Europe – and could be catastrophic for Ukraine. It was meant to be a patching up of the notoriously fraught Macron-Scholz relationship, a “reset”, to borrow Hillary Clinton’s expression.


“Broken” Franco-German tandem needs Tusk and Trump
As the vital relationship between Franco-German leaders Olaf Scholz and Emmanuel Macron appears “broken”, hopes for a sustainable fix rest on the Weimar Triangle and even the return of an old nemesis.


Macron and Scholz Meet to Patch up Their Fraying Ties
Allies fret that Franco-German animosity is undermining western unity over Ukraine. Emmanuel Macron will arrive in Berlin on Friday for talks designed to repair a fractured Franco-German relationship marred by caustic public spats and mutual recriminations over the war in Ukraine.
Electric Vehicles: A Strong and Still Understated Performance
Electric vehicles (EVs) are better for the climate – even in worst-case scenarios. Across its life cycle, a typical European electric car produces less greenhouse gas (GHG) and air pollutants or noise than its petrol or diesel equivalent. Emissions are usually higher in the production phase, but these are more than offset over time by lower emissions in the use phase. According to the European Environment Agency’s report on electric vehicles, life cycle GHG emissions of EVs are about 17-30% lower than those of petrol and diesel cars.
Without a Pact with Mercosur, the EU risks leaving China free in South America
The agreement EU-Mercosur It has been a banner of the recent protest by French farmers, who denounced unfair competition on the part of South Americans. However, if Paris closes the door to this pact, the way will be left clear to China, warn politicians and analysts consulted by EFE.
‘‘Jusqu’ici, tout va bien’’ ? A Cross-Analysis of Protest Cultures in France and Germany
The influence of different protest cultures on democracy in Germany and France is complex. The protest takes various forms, serves as political representation, and contributes to the formation of political opinion.
Thorns and Alliances. German, French and European Agricultural Policy Between Food Safety and Respect for the Environment
Influences and developments within German agricultural policy have undergone significant transformations over the past 70 years, especially in the context of the dynamic Franco-German relations and the pivotal role both nations play in shaping the European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP).
Troubled Twins: The FCAS and MGCS Weapon Systems and Franco-German Co-operation
The FCAS (Future Combat Air System) and the MGCS (Main Ground Combat System) represent the latest chapter in a more than seven decades-long history of Franco-German defense co-operation.

Malta: No Bridge is "A Bridge Too Far"
Malta as an isolated country saw relations with the EU as a bridge building effort with the peoples of the European Continent, which would also secure supplies, open markets, help obtain energy and strengthen security.

Italy: Wavering Between Europhilia and Euroscepticism
Italy has gone from one of the most pro-EU country to a rather euro-critical one. The crisis has dimmed hopes that the EU membership was a stimulator for economic growth. Moreover, Italians believed that the EU would be able to correct the shortcomings of national institutions. Phenomena, such as corruption, however, remain acutely perceived in Italy.

Hungary: Not Such a Black Sheep Within the EU
Despite a heavy toll in some sectors, Hungary has managed to reap the benefits of membership to the EU via the Structural Funds and access to the single market. The freedom of movement has also become a treasured right among Hungarians, for leisure and for jobs – about 500,000 have gained employment in other European countries.

Bulgaria: The Spectre of a Two-Speed Europe
One of Bulgaria’s paradoxes is that 25 years after the collapse of communism and almost ten years of EU membership, it seems to be quite unhappy with the transition but rather happy with its EU membership. In this way, the EU continues to be a beacon outside rather than the reality inside the country.

Portugal: Waiting for Better in the Adversity
The Portuguese population remains supportive of the EU, but without a clear motive, and with a feeling that the country is run by external actors with external interests. Meanwhile, the authorities have strived to appear as “a good student” rigorously implementing austerity measures.

Belgium: A Discreet and Pragmatic Europhile Approach
Belgium has historically been a pro-European country. It depends on trade and foreign investment. As a small country, it benefits from being part of an institutional framework that balances the power of bigger Member States. The lack of a strong sense of national identity also helps to explain why there has been less reluctance to transfer competences to the EU.

Sweden: Mind Rather Than Heart in EU Politics
The Swedish decision to enter the EU was not based so much on the hope of gaining something, but rather on the fear of being left out if it did not. It was probably the desire for a ‘negative safety’ that made the Swedes vote in favour of the EU as the alternative cost would probably have been too high.

Austria: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Due to geopolitical constellations, Austria could be seen as “a rather late” comer to the European Union (it joined in 1995). The rationale to join remains relevant: protection of wealth and securing a prosperous future. Being very reliant on export, the access to the single market is fundamental to its economy. The enlargement has also helped Austria become a hub between Western and Eastern Europe.

Latvia: Supporting the Right Cause and Deepening the Economic and Monetary Union
Latvia’s benefits to the EU have been clear. It has boosted the modernisation of the country and its infrastructures via the Cohesion Funds. It has helped reconnect the country with the West. And it has served to provide security to Latvia, especially vis-à-vis Russia.

Denmark: A Pragmatic Euroscepticism
The Danes are generally happy with the EU’s level of economic integration and are proponents of furthering the integration of the single market. However, they are sceptical when it comes to the EU’s federal trimmings and EU process standards in social and employment policies.
Support independent French research
Ifri, a foundation recognized as being of public utility, relies largely on private donors – companies and individuals – to guarantee its sustainability and intellectual independence. Through their funding, donors help maintain the Institute's position among the world's leading think tanks. By benefiting from an internationally recognized network and expertise, donors refine their understanding of geopolitical risk and its consequences on global politics and the economy. In 2024, Ifri will support more than 70 French and foreign companies and organizations.